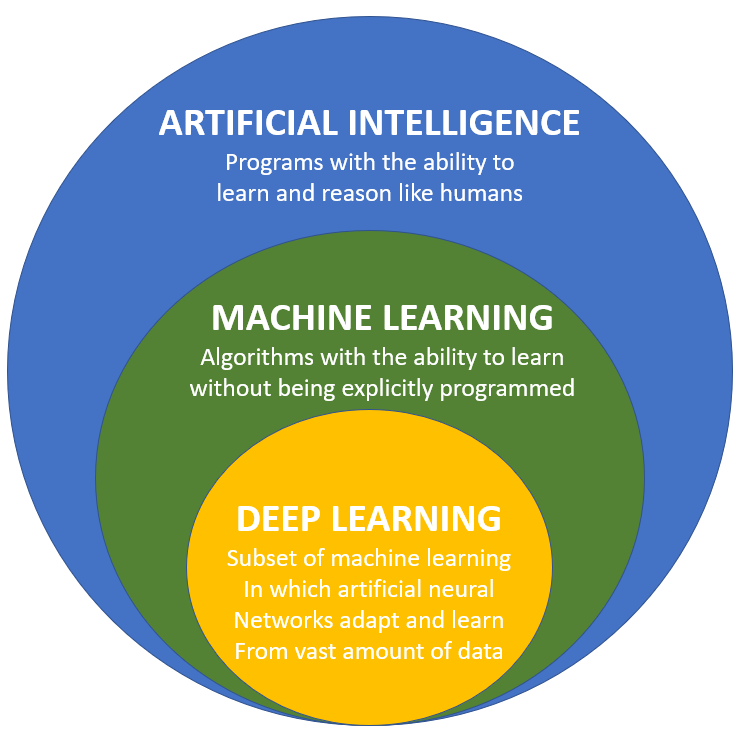
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the field of computer science dedicated to solving cognitive problems commonly associated with human intelligence, such as learning, problem solving, and pattern recognition. Artificial Intelligence, often abbreviated as "IoT", may connote robotics or futuristic scenes, AI goes well beyond the automatons of science fiction, into the non-fiction of modern day advanced computer science. Interest in artificial intelligence (AI) is increasing day by day. When the word artificial intelligence is used in the press or media, it is often seen that the words Machine Learning and Deep Learning are accompanied. Machine learning and deep learning are known as sub-concepts of artificial intelligence, but in this post, I will summarize the differences with specific examples.
Machine learning is a branch of artificial intelligence (AI) and computer science which focuses on the use of data and algorithms to imitate the way that humans learn, gradually improving its accuracy. Machine learning is the job of a program to learn from a lot of data and analyze patterns. It aims to increase prediction accuracy by finding the most reasonable model (correlation expression) while reducing errors (the difference between the predicted result Y-hat and the actual Y) during the learning process.
Deep Learning is a branch of machine learning that involves layering algorithms in an effort to gain greater understanding of the data. The algorithms are no longer limited to create an explainable set of relationships as would a more basic regression. Instead, deep learning relies on these layers of non-linear algorithms to create distributed representations that interact based on a series of factors. Given large sets of training data, deep learning algorithms begin to be able to identify the relationships between elements. These relationships may be between shapes, colors, words, and more. From this, the system can then be used to create predictions. Within machine learning and artificial intelligence, the power of deep learning stems from the system being able to identify more relationships than humans could practically code in software, or relationships that humans may not even be able to perceive. After sufficient training, this allows the network of algorithms to begin to make predictions or interpretations of very complex data.

As mentioned above, deep learning falls under the subcategory of machine learning. If so, it is necessary to examine the specific differences between machine learning and deep learning.
The difference between machine learning and deep learning is that there is a performance difference depending on the amount of data. As you can see in the example above, deep learning directly finds important features to solve a given problem. Therefore, in the case of deep learning, if the amount of data is not sufficient, the performance is limited. On the other hand, given enough data, it is possible to find more important features that humans are not aware of, often with better performance.
Deep learning can learn data to be used for classification by itself, whereas machine learning can process training data or learn only information about specific features. In order to classify dogs and cats, humans think the shape of the ears is important, and it can be used for machine learning by converting this information into data. However, deep learning looks for features that better differentiate between dogs and cats, such as the length of the tail. This may not be perceived by humans when thinking, but it can have a greater impact on actual classification performance, and deep learning can learn these important points on its own.